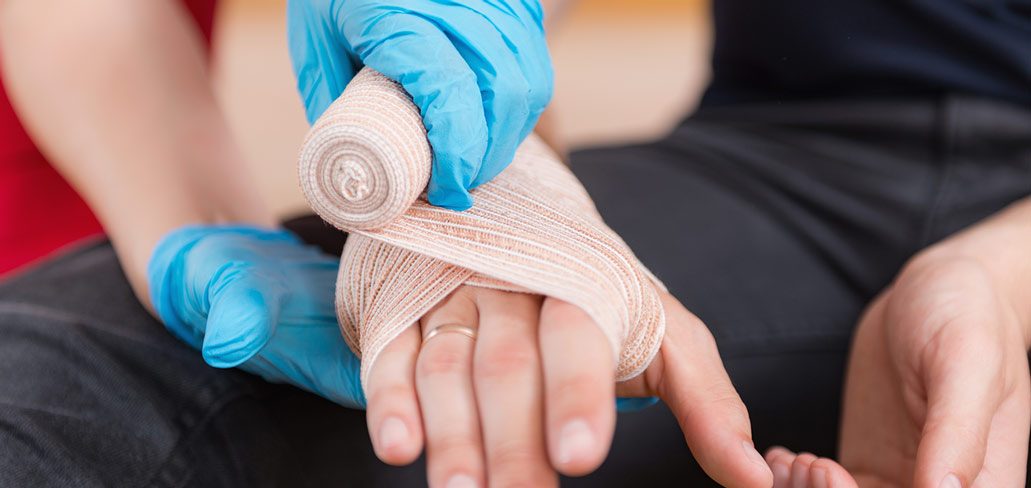
Wound Care for PCTs: Dressings, Cleaning, & Infection Signs
Wound care is a crucial aspect of patient care, and Patient Care Technicians (PCTs) play a vital role in this process. Understanding different types of dressings, proper cleaning techniques, and recognizing signs of infection are essential skills for PCTs to ensure effective wound healing and prevent complications.
Understanding Wound Types:
Before diving into dressings and cleaning, it’s important to understand the basics of wound types. Wounds can be classified as:
- Acute Wounds: These are typically caused by injury or surgery and heal within a predictable timeframe.
- Chronic Wounds: These wounds fail to heal within the expected timeframe, often due to underlying medical conditions like diabetes or poor circulation.
Different Types of Dressings:
Choosing the right dressing is crucial for promoting wound healing. PCTs should be familiar with various dressing types and their applications:
- Gauze: A versatile and cost-effective dressing used for cleaning and covering wounds. It comes in various forms, including pads, rolls, and sponges.
- Transparent Film Dressings: These dressings are waterproof and allow for visual inspection of the wound without removing the dressing. They are often used for superficial wounds.
- Hydrogel Dressings: These dressings are gel-based and provide moisture to the wound bed, making them suitable for dry wounds or burns.
- Hydrocolloid Dressings: These dressings create a moist environment that promotes healing and can be used for wounds with light to moderate drainage.
- Foam Dressings: These dressings are highly absorbent and are ideal for wounds with moderate to heavy drainage.
- Alginate Dressings: Made from seaweed, these dressings are highly absorbent and are used for wounds with heavy drainage.
- Antimicrobial Dressings: These dressings contain antimicrobial agents to help prevent infection.
Cleaning Techniques:
Proper wound cleaning is essential to remove debris, bacteria, and other contaminants that can impede healing. Here are some key steps:
- Hand Hygiene: Meticulous hand hygiene is paramount before and after any wound care procedure.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves, to protect yourself and the patient.
- Cleaning Solution: Use a prescribed cleaning solution, which may include sterile saline, wound cleanser, or diluted antiseptic solution. Never use harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide or iodine unless specifically ordered by a physician, as these can damage tissue.
- Cleaning Method: Gently cleanse the wound using a gauze pad or cotton swab, moving from the inside out to avoid reintroducing bacteria. For deeper wounds, irrigation may be necessary.
- Drying the Wound: Pat the surrounding skin dry with a clean gauze pad. Avoid rubbing the wound itself.
Applying Dressings:
- Choose the Right Dressing: Select the appropriate dressing based on the wound type, location, and drainage.
- Secure the Dressing: Secure the dressing with tape, gauze, or a bandage, ensuring it is snug but not too tight.
- Document the Procedure: Document the type of dressing used, the cleaning solution, and any other relevant information.
Recognizing Signs of Infection:
Early detection of infection is crucial to prevent complications. PCTs should be vigilant in observing for the following signs:
- Increased Pain: A sudden increase in pain at the wound site.
- Redness: Redness spreading around the wound edges.
- Swelling: Increased swelling or edema around the wound.
- Warmth: Increased warmth to the touch around the wound.
- Purulent Drainage: Thick, yellow or green drainage (pus).
- Fever: An elevated body temperature.
- Foul Odor: An unpleasant or unusual odor coming from the wound.
Reporting Concerns:
If you observe any signs of infection or other complications, it is crucial to report your findings to the nursing team immediately. Timely intervention can prevent the infection from spreading and promote healing.
Continuing Education:
Wound care practices are constantly evolving. PCTs should stay updated on the latest research and best practices through continuing education and training.
By understanding wound types, mastering cleaning and dressing techniques, and recognizing signs of infection, PCTs play a vital role in promoting wound healing and ensuring patient comfort. Your diligence and attention to detail are essential for preventing complications and optimizing patient outcomes.