Patient Safety & Fall Prevention: Creating a Safe Environment
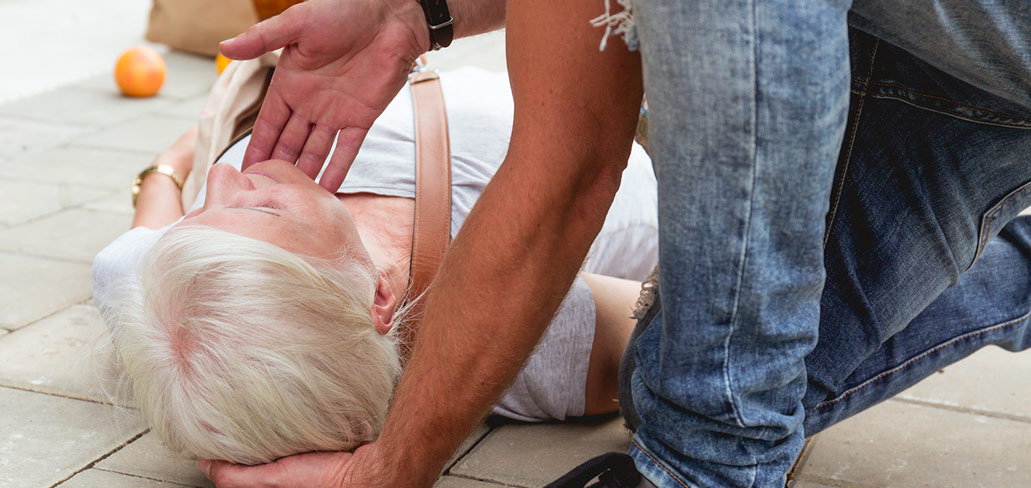
Patient falls are a significant concern in healthcare settings, posing risks to patient well-being and impacting overall quality of care. As Patient Care Technicians (PCTs), you play a crucial role in creating a safe environment and minimizing fall risks. This blog post outlines essential strategies for preventing falls and promoting patient safety.
Understanding the Risks:
Falls can have serious consequences, including fractures, head injuries, and even death. Understanding the common risk factors is the first step in prevention. These include:
- Age: Older adults are at increased risk due to age-related changes in balance, vision, and muscle strength.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, arthritis, and dementia, can increase fall risk.
- Medications: Some medications can cause dizziness, drowsiness, or postural hypotension, increasing the likelihood of falls.
- Previous Falls: A history of falls is a strong predictor of future falls.
- Environmental Hazards: Cluttered rooms, wet floors, and poor lighting can create tripping hazards.
- Functional Limitations: Weakness, impaired mobility, and difficulty with balance can contribute to falls.
Creating a Safe Environment:
PCTs are instrumental in creating a safe environment for patients. Here are some key strategies:
- Regular Rounds and Observation: Conduct frequent rounds to check on patients and identify potential hazards. Pay close attention to patients who are at high risk for falls.
- Clutter-Free Environment: Keep patient rooms and hallways free of clutter. Ensure that pathways are clear and unobstructed.
- Proper Lighting: Adequate lighting is essential for preventing falls. Ensure that rooms and hallways are well-lit, especially at night.
- Clean and Dry Floors: Clean up spills immediately and ensure that floors are dry and free of hazards. Use “wet floor” signs to warn others of potential dangers.
- Assistive Devices: Ensure that patients have access to and use appropriate assistive devices, such as walkers, canes, or wheelchairs. Make sure these devices are in good working order.
- Bed and Chair Alarms: Utilize bed and chair alarms for patients who are at high risk for falls. These alarms can alert staff when a patient attempts to get out of bed or a chair unassisted.
- Side Rails: Use side rails judiciously, as they can sometimes pose a risk if not used properly. Consult with the nursing team to determine the appropriate use of side rails for individual patients.
- Call Lights Within Reach: Ensure that call lights are within easy reach for patients. Educate patients on how to use the call light to request assistance.
- Low Beds: For patients at high risk for falls, consider using low beds to minimize the distance to the floor in case of a fall.
Minimizing Risks Through Patient Care:
Beyond creating a safe environment, PCTs play a critical role in minimizing fall risks through direct patient care:
- Fall Risk Assessment: Be aware of patients who have been identified as being at high risk for falls. Review their care plans and implement appropriate fall precautions.
- Assisting with Mobility: Assist patients with ambulation, transfers, and other activities as needed. Never allow a patient to ambulate alone if they are at risk for falls.
- Education: Educate patients and their families about fall prevention strategies. Provide information on how to create a safe environment at home.
- Medication Management: Be aware of the potential side effects of medications that can increase fall risk. Communicate any concerns to the nursing team.
- Toileting Assistance: Offer regular toileting assistance to patients to prevent falls related to urgency or nocturia (nighttime urination).
- Proper Footwear: Encourage patients to wear comfortable, non-slip footwear.
- Exercise and Strength Training: Promote exercise and strength training programs to improve balance and mobility. Consult with physical therapy for appropriate exercises.
Documentation and Communication:
- Document all falls: If a patient does fall, document the incident thoroughly, including the time, location, and circumstances of the fall.
- Communicate with the team: Communicate any concerns about patient safety or fall risks to the nursing team and other members of the healthcare team.
A Proactive Approach:
Preventing falls requires a proactive and collaborative approach. By understanding the risks, creating a safe environment, and providing patient-centered care, PCTs can significantly reduce the incidence of falls and promote patient safety. Remember, every interaction is an opportunity to assess for fall risks and intervene appropriately. Your vigilance and dedication to patient safety make a real difference!